Knee Arthroscopy
Articular Cartilage Problems
Removal of Damaged Cartilage
Articular cartilage is a firm rubbery tissue that covers the ends of bones. It provides a smooth gliding surface for joints and acts as a cushion between bones.
Microfracture
After the damaged cartilage is removed, a drill or pick is used to make small holes in the exposed bone. Making these small holes will help heal the damaged area, thus the term “drilling/microfracture”.
Cartilage Transplants: Autograft (from you)
Healthy bone and cartilage is taken from a non-weight bearing section of your femur. The damaged area is prepared and the new tissue plug is inserted into the site.
Cartilage Transplants: Allograft (from cadaver)
A plug of allograft tissue containing bone and cartilage is shaped to fit into the area that is damaged. The damaged area is prepared and the new tissue plug is inserted into the site.
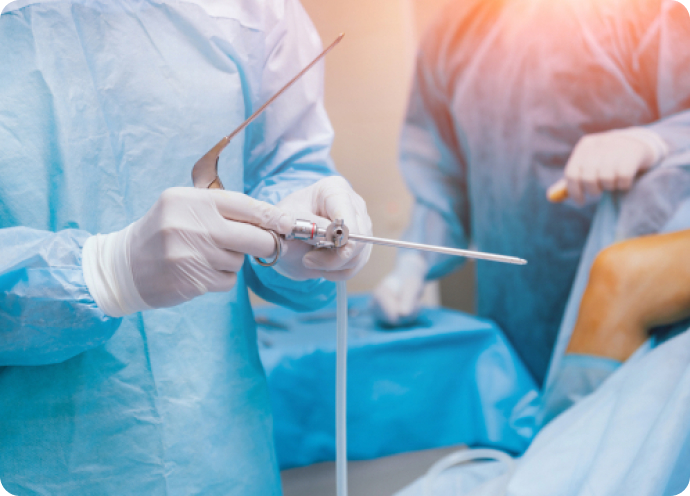
Diagnostic Arthroscopy
Diagnostic Arthroscopy
Arthroscopic surgery allows diagnosis and treatment of joint problems through small incisions in the skin. A camera attached to a scope is used to see inside your joint.
Joint Replacement
Partial Knee Replacement
Partial Knee Replacement (also known as Uni Knee Replacement) involves resurfacing the damaged portions of the knee while leaving healthy areas intact. The cartilage covering the femur and tibia becomes worn and the underlying bone develops spurs and various irregularities which produce pain and loss of knee motion. This procedure is most commonly performed on the inside (medial) section of the knee but in some cases it may also be performed on the outside (lateral) section of the knee as well.
Revision Knee Replacement
With wear, the original components of a Total Knee Replacement break down and loosen from the bone surface they were once firmly attached to. Revision Knee Replacement involves the exchange of some or all worn components of the primary Total Knee Replacement. The breakdown of the original components and loosening from the bone surfaces causes pain in the joint. Your doctor will determine the degree of complexity for this procedure based on the amount of loosening and associated damage to the underlying bone surfaces that may have occurred over time.
Total Knee Replacement
Total Knee Replacement is performed to remove the degenerated and worn portions of the knee and reposition it into normal alignment. New components will be implanted into the knee to replace the worn-out bone and cartilage. Implant components can be made of metal, polyethylene plastic or ceramic material. In cases requiring total knee replacement, the cartilage covering the femur, tibia, and patella becomes worn and the underlying bone develops spurs and various irregularities which produce pain and loss of knee motion.
Loose Bodies
Loose Bodies
Loose bodies are another name for free floating pieces of debris in the joint. They are tissues that have torn away from their original location and move around the joint causing pain, swelling and locking.
Patella (Knee Cap) Pain
Drilling/Microfracture of Damaged Articular Cartilage
The patella is a flat triangular shaped bone that protects the knee joint and helps muscles move your leg more efficiently. A healthy patella glides up and down a groove at the end of your femur, pain free.
Drilling/Microfracture of Damaged Articular Cartilage
The patella is a flat triangular shaped bone that protects the knee joint and helps muscles move your leg more efficiently. A healthy patella glides up and down a groove at the end of your femur, pain free.
Removal of Damaged Articular Cartilage
The patella is a flat triangular shaped bone that protects the knee joint and helps muscles move your leg more efficiently. A healthy patella glides up and down a groove at the end of your femur, pain free.
Removal of Painful Plica
The patella is a flat triangular shaped bone that protects the knee joint and helps muscles move your leg more efficiently. A healthy patella glides up and down a groove at the end of your femur, pain free.


Synovial Problems
Removal of Inflamed Synovium
The synovium membrane is found in joints like your knee and shoulder. This thin membrane surrounds the inner lining of your joint and may have folds and fringes. Its main function is to create synovial fluid which helps nourish and lubricate your joint.
Removal of Painful Plica
The synovium membrane is found in joints like your knee and shoulder. This thin membrane surrounds the inner lining of your joint and may have folds and fringes. Its main function is to create synovial fluid which helps nourish and lubricate your joint.
Torn ACL
Allograft Graft
A guide wire is inserted through the tibia and femur to help accurately drill tunnels. A surgical drill is inserted over the guide wire and a new tunnel in the femur and tibia is created for your new ACL Graft. The end of the graft is tied to a loop on the guide wire and the graft is pulled into place.
Bone-Patellar Tendon-Bone Graft
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four ligaments that are crucial to the stability of your knee. It is a strong fibrous tissue that connects the femur to the tibia. A partial or complete tear of your ACL will cause your knee to become less stable and feel as though your knee is about to give out. There are a number of different graft options to replace your torn ACL. Your surgeon will select the option that is best for you.
Hamstring Graft
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four ligaments that are crucial to the stability of your knee. It is a strong fibrous tissue that connects the femur to the tibia. A partial or complete tear of your ACL will cause your knee to become less stable and feel as though your knee is about to give out. There are a number of different graft options to replace your torn ACL. Your surgeon will select the option that is best for you.
Quadriceps Tendon Graft
A guide wire is inserted through the tibia and femur to help accurately drill tunnels. A surgical drill is inserted over the guide wire and a new tunnel in the femur and tibia is created for your new ACL Graft. The end of the graft is tied to a loop on the guide wire and the graft is pulled into place.

Torn Meniscus
Torn Meniscus Repair
A healthy meniscus acts as a shock absorber and provides a smooth surface for your knee to glide on. A meniscal tear prevents your knee from rotating causing pain and locking.
Torn Meniscus Trimming
A healthy meniscus acts as a shock absorber and provides a smooth surface for your knee to glide on. A meniscal tear prevents your knee from rotating causing pain and locking.
